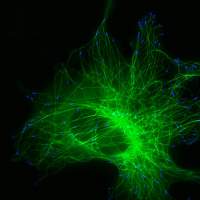
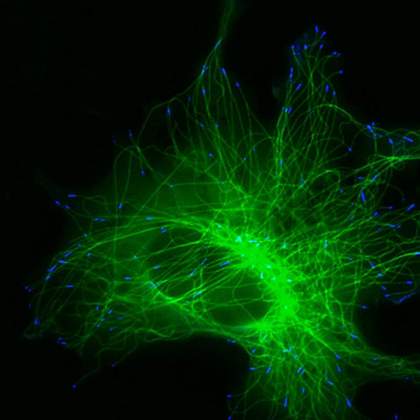
Are you a journalist? Please sign up here for our press releases
Subscribe to our monthly newsletter:
Are you a journalist? Please sign up here for our press releases
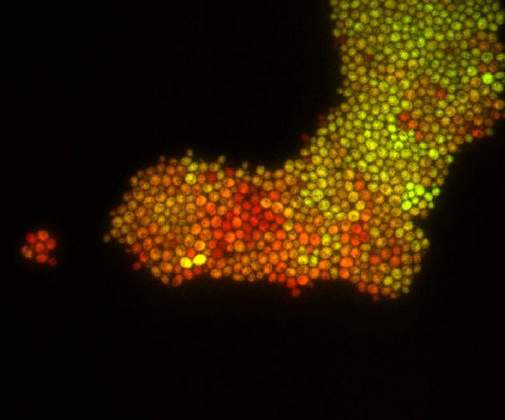
Pearl Girl | Dr. Maya Dadiani, Departments of Molecular Cell Biology & Computer Science. Fluorescent yeast cells growing in a monolayer on a microfluidic platform. The cells divide and their colonies sometimes create funny shapes. The cells express two fluorescent proteins, yellow and green, on different levels.
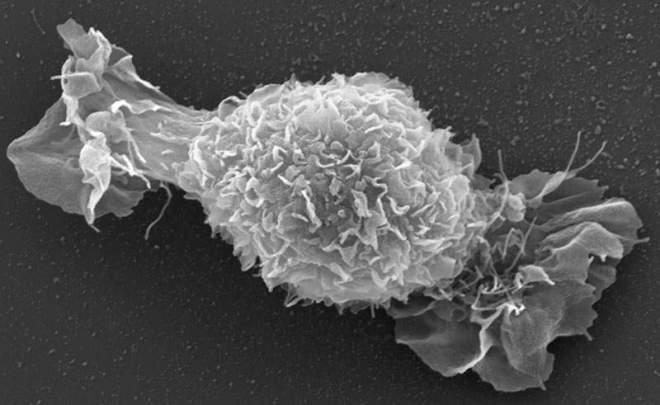
Sweet Science | Dr. Miriam Cohen and Prof. Lia Addadi, Department of Structural Biology. Rat Chondrocyte spreading on a glass surface. The spreading lamellipodia gave the cell a candy-like appearance.
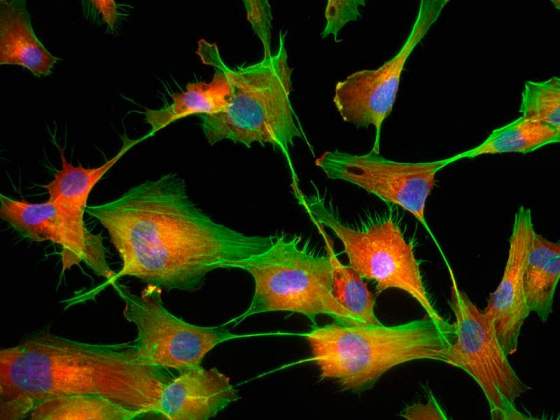
BBB: Endothelium | Itzik Cooper, Department of Neurobiology. The Blood-Brain Barrier (BBB) restricts the entry of unwanted compounds (and unfortunately sometimes beneficial molecules like drugs) to the brain. The BBB is composed of capillaries made of endothelial cells ensheathed with Astrocytes. The endothelial cells shown in this picture provide the “first line of defense” to the brain.
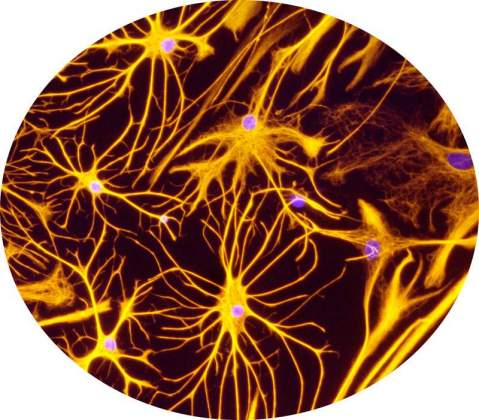
BBB: Astrocytes | Itzik Cooper and Dr. Keti Cohen-Kashi Malina, Department of Neurobiology. The Blood-brain barrier (BBB) restricts the entry of unwanted compounds (and unfortunately sometimes wanted molecules like drugs) to the brain. The BBB is composed of capillaries made of endothelial cells ensheathed with Astrocytes. The Astrocytes ("star-like") cells shown in this picture provide the biochemical support to the endothelial cells, together forming the BBB.
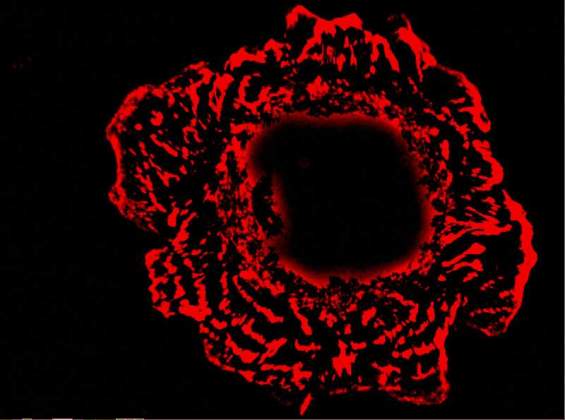
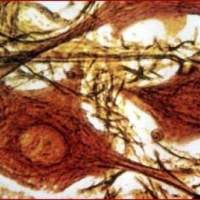
Rose | Dr. Tova Volberg, Department of Molecular Cell Biology. A cell labeled with red fluorescent antibodies against the vinculin protein.
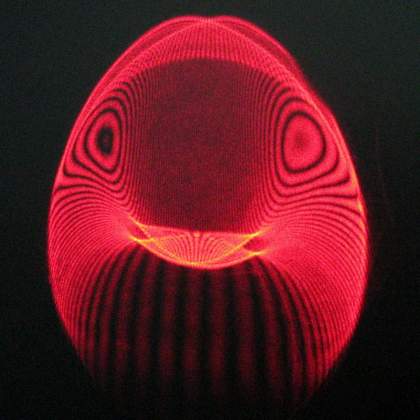

The Swallow | Oren Raz and Dr. Rami Pugach, Department of Physics of Complex Systems. A small fraction of laser light had escaped from our experimental setup and expressed it's freedom in a shape of a swallow on the next wall.
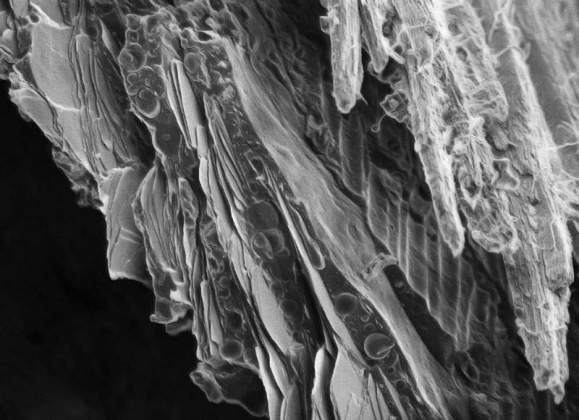
The Koi Fish | Dvir Gur, Department of Structural Biology. An up close view of the Koi fish scale. On the left are the guanophores, cells that contain guanine crystals. The arrangement of the guanine crystals inside the tissue causes special interactions between the crystals and the light, resulting in the brilliant colors of the Koi fish. This image was taken using a scanning electron microscope at -120°C.
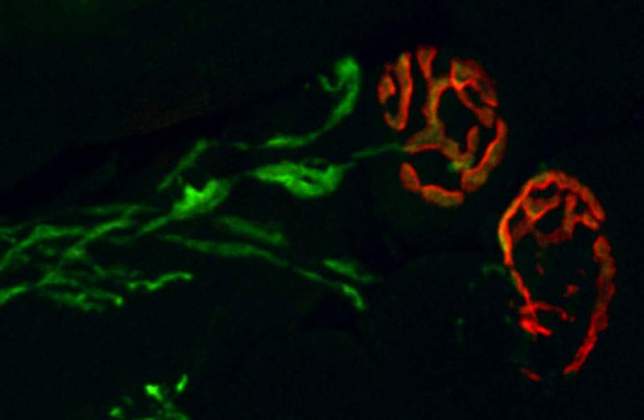
The Rose That Moves You | Kfir Umansky, Department of Molecular Genetics. This is a picture of a neuromuscular junction – the junction (synapse) that connects and allows the interaction between muscle and the motor neuron (nerve) that “tells” it to contract and move. The nerve extension into that junction is depicted in green and the muscle part of the synapse is depicted in red.
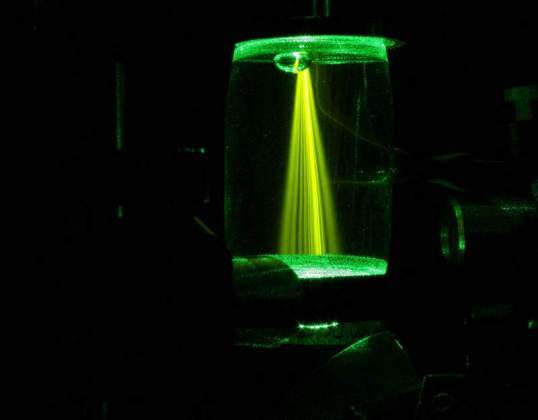

Illuminating Randomness | Yoav Lahini, Yaron Bromberg, Adi Natan and Prof. Yaron Silberberg, Department of Physics of Complex Systems. Scattered light can create random interference patterns ('speckles') which carry information on the structure that scattered the light. Scientists have found clever ways to extract this information. The image shows the propagation of scattered light trough a florescent chamber, in an effort to better understand this effect.
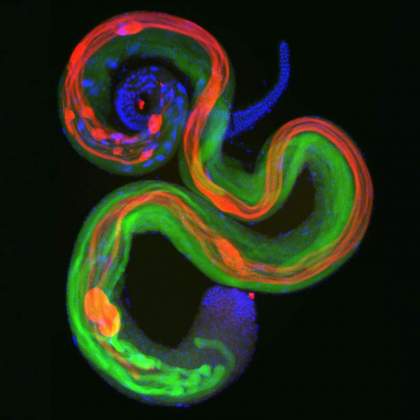
The Death Movement | Yosef Kaplan, Department of Molecular Genetics. Caspases, the executioners of programmed cell death, participate in the elimination of the cytoplasmic contents of the sperm cells during their maturation. This image demonstrates the 2 mm long developing sperm cells of the fruit fly Drosophila (nuclei in blue) and active caspases (in red). Caspase activation during this vital process is highly restricted in space and time by regulatory proteins (green).
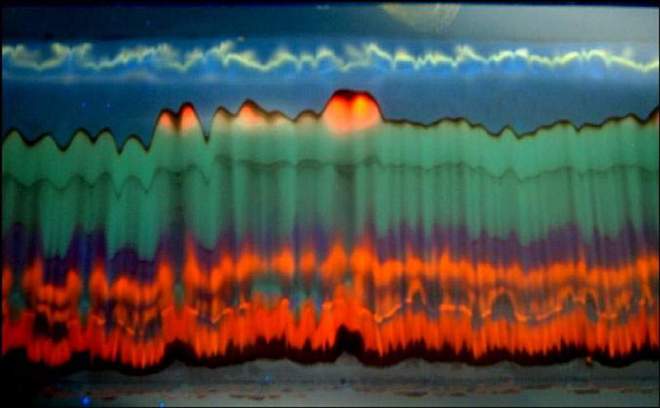
Burning Waves Under The TLC Sky | Dr. Haim Weissman, Department of Organic Chemistry. The image is a luminescent result of an exposure to UV light of a Thin Layer Chromatographic (TLC) separation plate containing a separated crude reaction mixture of ruthenium terpyridine complexes. The different compounds that were separated on the plate during the chromatographic process luminesce in different colors.
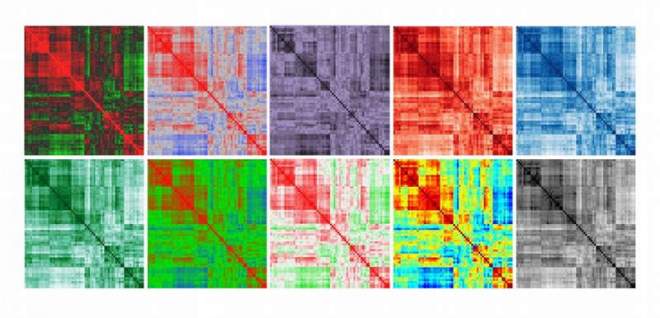
A Study of Mass (Spec) Production in Art. | Dr. Vered Tzin and Dr. Samuel Bocobza, Department of Plant Sciences. Here, the biological data of a tomato metabolic profile is represented in the most possible simplistic fashion. In this series of Heat Maps, the omnipresence of data reduction results in the loss of biological significance.
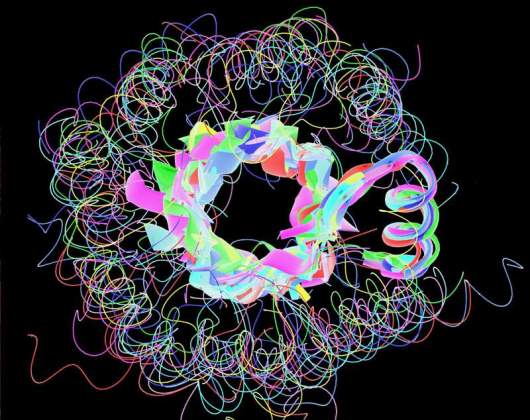
TIM Beta-Barrel Proteins | Prof. Shmuel Pietrokovski, Department of Molecular Genetics. Using a sensitive method we developed to compare protein sequence motifs we identified a set of 10 motifs. All motifs have the same structure and are part of proteins that have an overall fold called TIM beta-barrel.
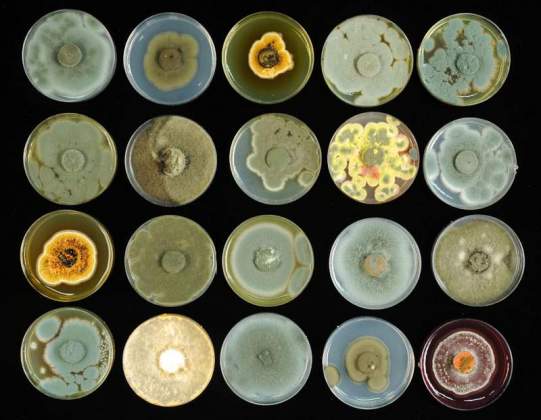

The Art of the Fungi | Naama Lang-Yona, Department of Environmental Sciences and Energy Research; Ohad Herches, Photography. The world of fungi existing in our surrounding air is rich and diverse. Some may encourage disease or allergies, while other assist healing. The pictures show different fungi species sampled from the air during springtime in Rehovot, Israel. The fungal spores or their secreted metabolites together create the colorful combination.
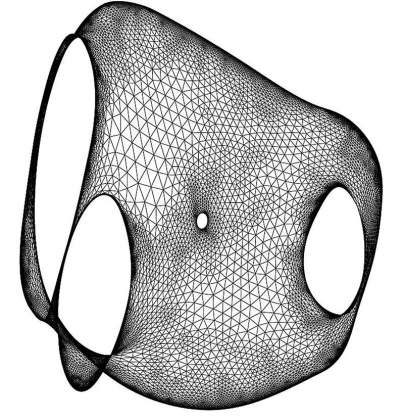
Automatic Aesthetic Drawing of Large Graphs | Prof. David Harel, Department of Computer Science and Applied Mathematics. These are images taken from work done with Yehuda Koren in 2001-2003 on algorithms for "graph layout". The algorithm figures out how to place the graph vertices in the two-dimensional geometric plane so that the outcome is “nice” and “aesthetic”.
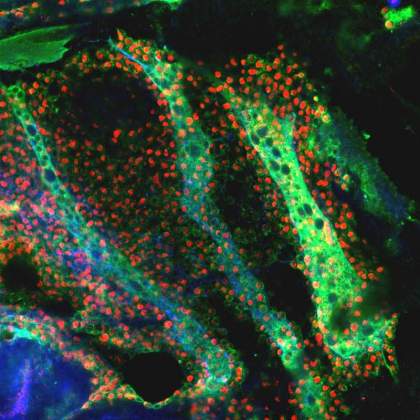
The Swarm | Boaz Gildor, Department of Molecular Genetics. The developing flight muscles of the fruit fly during metamorphosis. The larval muscles (marked by blue and green) serve as templates and send an attraction signal towards the muscle cell swarm (marked by red and green). The cells react to this signal and migrate towards the muscle templates. Eventually, each cell will fuse to the templates, giving rise to the adult flight muscles.
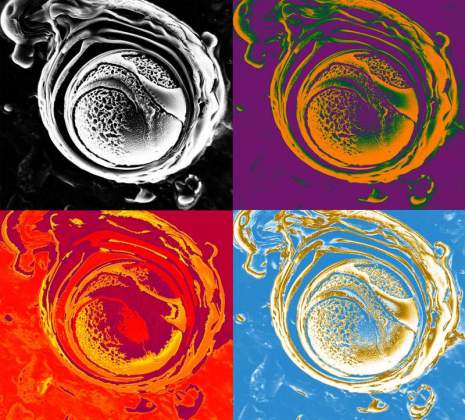
Pop Art Liposom | Dvir Gur, Department of Structural Biology. A multi-layer vesicle made from lipids. The vesicle encapsulates guanine, a nucleic acid, within it. This vesicle was made in an attempt to mimic the micro environment in which guanine crystals are formed in organisms such as fish and spiders, which use the special properties of guanine crystals in order to form structural colors. This is an electron microscope image taken at -120°C.
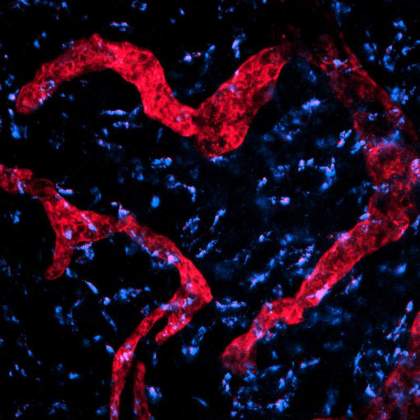
Lovely Lymphatics | Irina Gurevich, Department of Immunology. The image depicts lymphatic vessels (red) and some protein signaling molecules (blue) in a deep layer of a mouse skin (dermis). The vessels and the proteins were stained with specific fluorescent dyes, which allowed to visualize particularly the arrangement of those structures using a fluorescent microscopy technique.
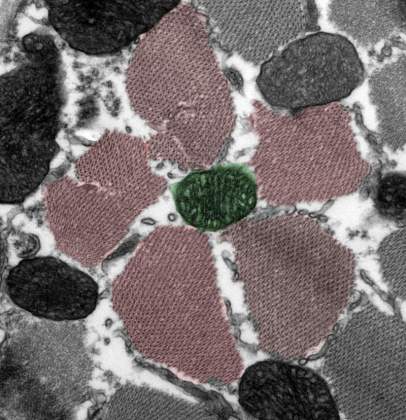
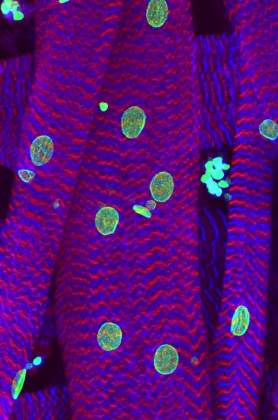
The Mutant Flower | Dr. Yael Gruenbaum-Cohen, Department of Molecular Genetics. Skeletal muscle is made up of individual components known as muscle fibers. Under normal conditions these fibers are aligned in close proximity to each other. In this electron tomography picture, we encaptured a cross section of a mutant mouse, who is suffering from a muscle degenerative disease (myopathy).
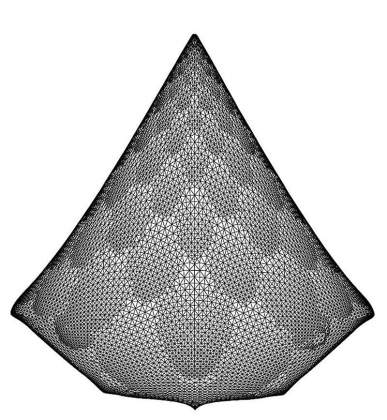
Automatic Aesthetic Drawing of Large Graphs | Prof. David Harel, Department of Computer Science and Applied Mathematics These are images taken from work done with Yehuda Koren in 2001-2003 on algorithms for "graph layout". The algorithm figures out how to place the graph vertices in the two-dimensional geometric plane so that the outcome is “nice” and “aesthetic”.
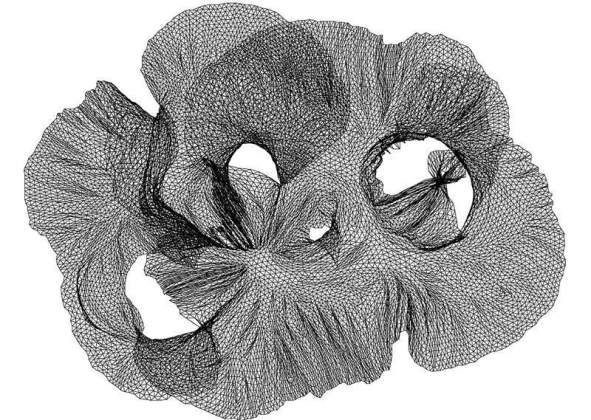

Automatic Aesthetic Drawing of Large Graphs | Prof. David Harel, Department of Computer Science and Applied Mathematics These are images taken from work done with Yehuda Koren in 2001-2003 on algorithms for "graph layout". The algorithm figures out how to place the graph vertices in the two-dimensional geometric plane so that the outcome is “nice” and “aesthetic”.
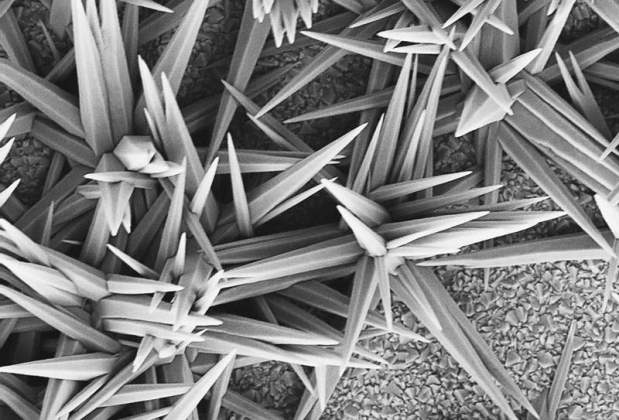
Porcupine ZnO | Eran Edri, Department of Materials and Interfaces. Zinc Oxide (ZnO) is a semiconductor which we use in our research as an electron carrier on photovoltaic cells. We deposit the ZnO from a solution and it usually grows as a rod-like film structure. Here, the ZnO rods had no interference to grow in all directions, which resulted in a porcupine-like structure.
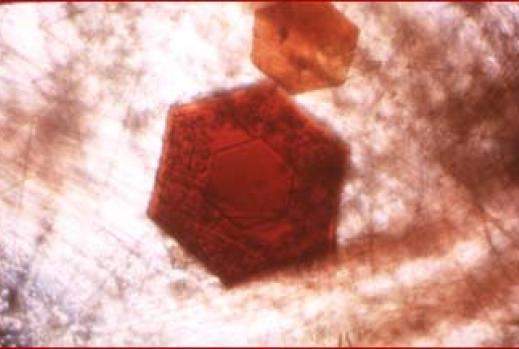
Paradoxin protein crystals | Dr. Felix Frolow, Department of Structural Biology Department.
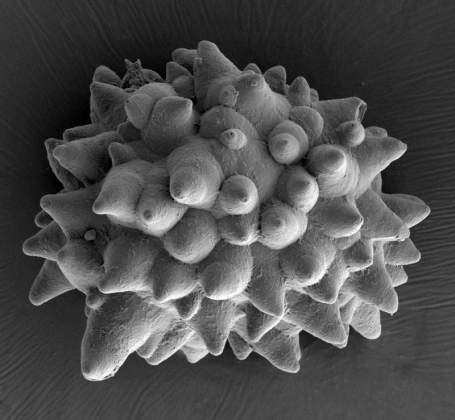
Ficus Leaf Mineral | Assaf Gal, Department of Structural Biology. Ficus tree leaves, as many other plants, contain various minerals. This scanning electron microscope image shows a calcium carbonate body called cystolith. The cystolith function is to scatter light in the leaf in order to help photosynthesis.
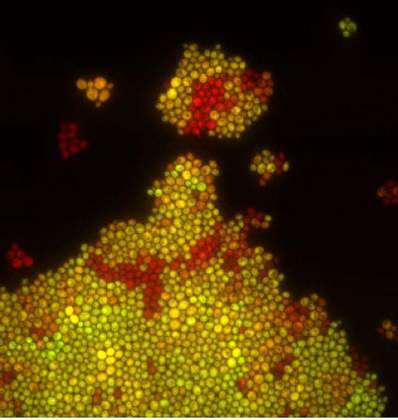
Pearl Girl | Dr. Maya Dadiani, Departments of Molecular Cell Biology & Computer Science. Fluorescent yeast cells growing in a monolayer on a microfluidic platform. The cells divide and their colonies sometimes create funny shapes. The cells express two fluorescent proteins, yellow and green, on different levels.
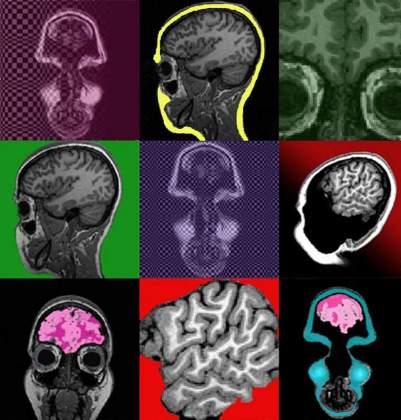
Brain Storm | Hagar Goldberg, Department of Neurobiology. MRI slices of the human brain, painted and presented as a tribute to Andy Warhol's Marilyn prints.
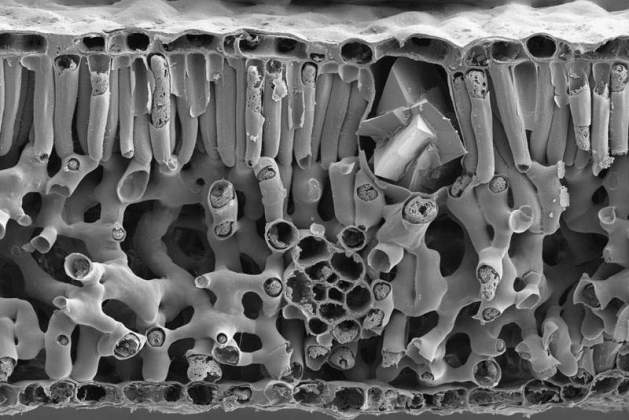
Cross Section in Pecan Leaf | Assaf Gal, Department of Structural Biology. A Pecan tree leaf was dried and fractured to reveal its internal structure. The image was taken with a scanning electron microscope showing the cells of the different tissues. On the upper right side of the leaf, a cell containing a calcium-oxalate crystal is visible.
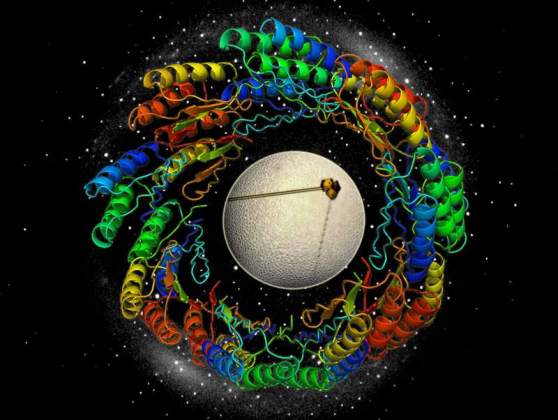

Structural Proteomics in Space and Time | Shelly Rogotner, Dr. Orly Dym and Prof. Joel Sussman, Israel Structural Proteomics Center (ISPC). The image describes the process of determining the three-dimensional protein structure (spirals), starting from protein crystals (shown in yellow) and their X-ray diffraction (white spots in the background).
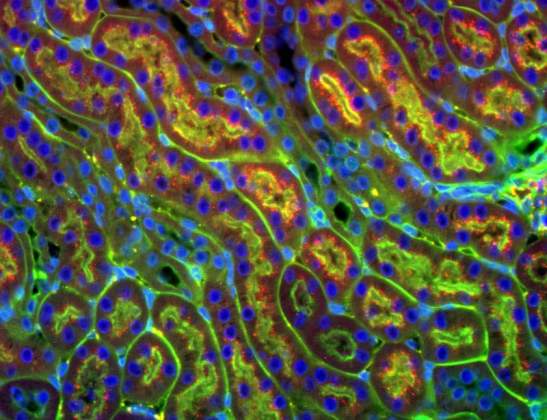
Chasing the Kidney | Dr. Hagit Dafni, Department of Biological Regulation. The high affinity between avidin (a protein abundant in egg-white) and biotin (a vitamin) was used to induce clearance (chase) of circulating molecules: circulating biothinyl-albumin (red) was first reabsorbed by the kidneys and later chased away from the blood by avidin (green). The cell nuclei are colored in blue.

Particle collision in a particle accelerator
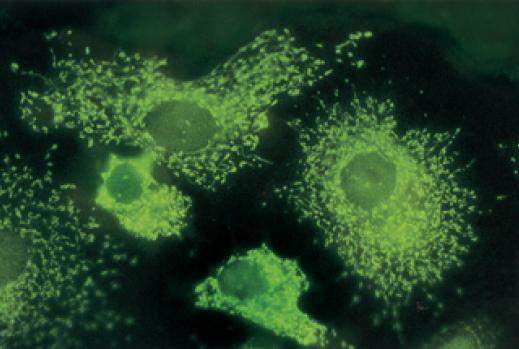
Ovarian cells, the manufacturers of female sex hormones like progesterone and estrogen.
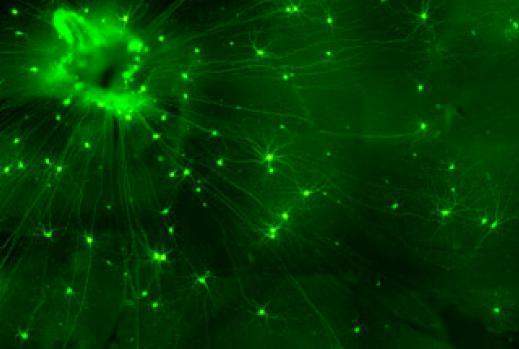
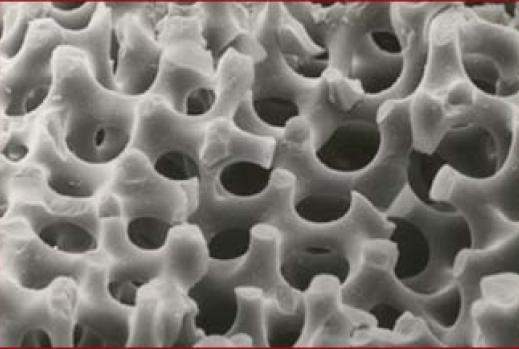
Needles of an Ascidian. Prof. Steve Weiner, Structural Biology Department
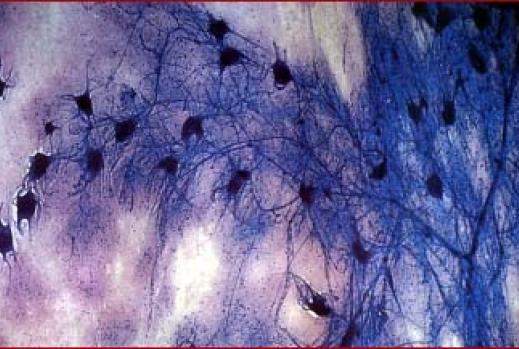
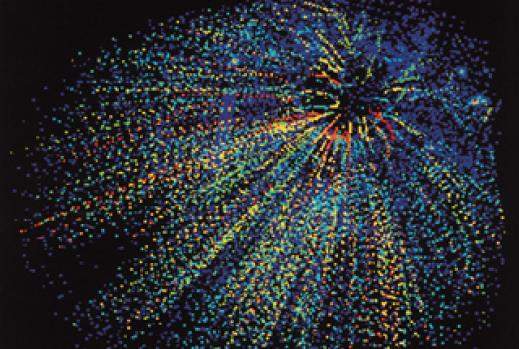
Particles emitted from the collision of one lead nucleus accelerated to almost the speed of light with a gold nucleus target at rest. Photographed at the European laboratory for particle physics.


Spatio-temporal chaotic patterns developing during the process of convection in gas under high pressure.

Spatio-temporal chaotic patterns developing during the process of convection in gas under high pressure.

Small boundary-layer eruptions occur during large-scale fluid motion caused by temperature variations in water.